
ASSESSMENT
Assessment will be based on one midterm exam and one final exam. The midterm exam will account for 40% of the overall grade, while the final exam will account for 60%. These exams will be comprehensive, with the final exam being particularly focused on practical applications.
ATTENDANCE
Regulations regarding attendance and absenteeism will be governed by the relevant student policies. Regular attendance is considered one of the most important criteria for success evaluation in this course.
RESOURCES
Büyüköztürk ŞENER.(2003). Sosyal Bilimler için Veri Analizi El Kitabı.Pegem Yayıncılık. ANKARA
Köklü, Nilgün & Büyüköztürk ŞENER.(2000) Sosyal Bilimlerde İstatistiğe Giriş. Pegem Yayıncılık. ANKARA
STATISTICS IN SOCIAL SCIENCES
The ability to make rational decisions, display consistent behaviors, and reach sound judgments is only possible through a thinking process based on accurate observation, experimentation, and testing. In this context, statistics is not merely a discipline concerned with numerical data; it is also the key to rational thinking, which forms the foundation of a correct, balanced, and well-grounded life.
OBJECTIVE
The primary aim of the statistics course in social sciences is to develop statistical thinking skills, which include competencies such as questioning, formulating hypotheses, testing hypotheses, relating results, providing justifications, and defending arguments based on scientific foundations.
In line with this objective, students are expected to acquire the following knowledge and experiences:
Introduction to the Research Process: The fundamentals of conducting research in the social sciences—formulating hypotheses, collecting data, analyzing data, and summarizing results through tables and graphs—will be addressed. Practical training will be provided on how these processes can be conducted using computer-assisted tools.
Descriptive Statistics: The course will introduce the concepts and operations of descriptive statistics, aiming to develop basic skills in summarizing and reporting data using the SPSS software.
Inferential Statistics: The course will present basic and intermediate-level inferential statistical methods, with an emphasis on applying these methods through SPSS and interpreting the resulting outputs.
Validity and Measurement: Students will learn to statistically evaluate the basic validity characteristics required of a measurement tool and perform these calculations within the SPSS environment.
This course is designed not only to equip students with technical knowledge but also to help them internalize the processes of scientific reasoning within the field of social sciences.
METHOD
This course will be conducted within a two-stage structure aimed at both understanding theoretical foundations and developing practical skills:
Stage One – Theoretical Preparation and Program Introduction:
In the initial weeks of the course, the fundamental concepts of statistical thinking, the steps of the research process, and the general structure of the SPSS software will be introduced. The SPSS user interface, basic menu options, data entry, and data editing procedures will be demonstrated through practical applications. This stage aims to equip students with a sufficient foundation for computer-assisted data analysis.
Stage Two – Applied Data Analysis:
In the second phase, students will work with various datasets to conduct analyses aligned with research questions and hypotheses. Over approximately ten weeks, students will perform descriptive and inferential analyses using SPSS; they will develop skills in interpreting results, organizing tables, and reporting findings. Throughout the course, practical learning through individual and group activities will be emphasized.
Time and Location:
Theoretical sessions and practical applications will be held on the days and times specified in the relevant academic program, within the designated classrooms.
Credit Information:
This course carries a weekly theoretical workload of 3 hours and totals 8 ECTS credits. The applications, individual assignments, and project work carried out within the course are included in the ECTS credit calculation.
SYLLABUS
Week 1 – Introduction and Getting Acquainted
Week 2 – Introduction to Statistics & Basic Concepts 1
Week 3 – Descriptive Statistics – Organizing Data
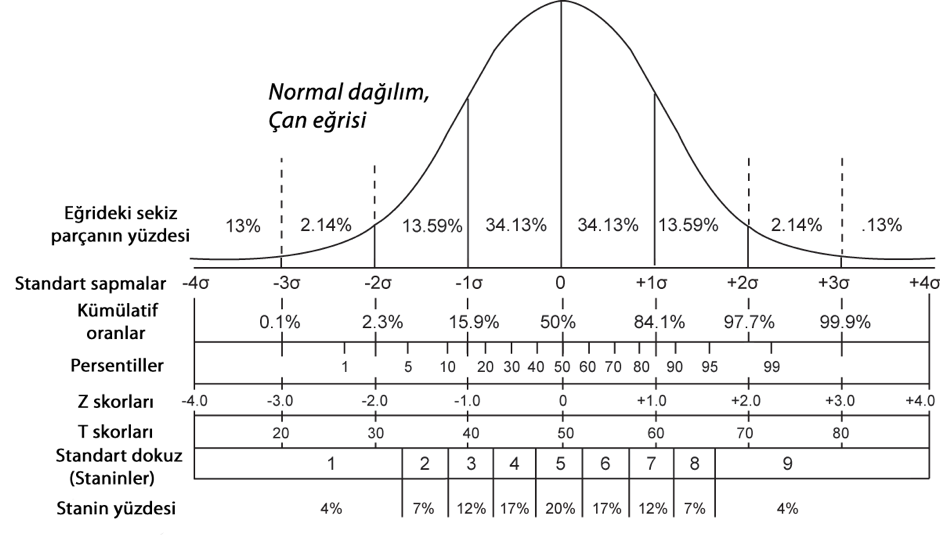
Week 4 - Merkezi Yığılma Ölçüleri, Normal Distribution and Standard Scores
Week 5 – Introduction to SPSS – Menus
Week 6 – Introduction to Inferential Statistics (Hypothesis Testing)
Week 7 – One-Sample, Independent-Sample, and Paired-Sample "T" & "Z" Tests
Week 8 – Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), and Covariance (ANCOVA)
Week 9 – M I D T E R M E X A M
Week 10 – Chi-Square (χ²) Test
Week 11 – Correlation Analysis: Bivariate and Partial Correlation
Week 12 – Practice
Week 13 – Nonparametric Tests
Week 14 – Practice
Week 15 - Practice
FINAL EXAM
SUPPLEMANTARY FILES TO STUDY:
Algorithms of Parametric Statistics
Kocaeli Üniversitesi, Eğitim Fakültesi, Eğitim Bilimleri Bölümü 41380 İzmit/Kocaeli/Türkiye
ismetsahin@gmail.com




